- Home
- HIGH PERFORMANCE PLASTICS
Description and properties of High Performance Plastics
High Performance Polymers are polymers which still perform well under extreme conditions. They are more demanding than standard and engineering plastics.
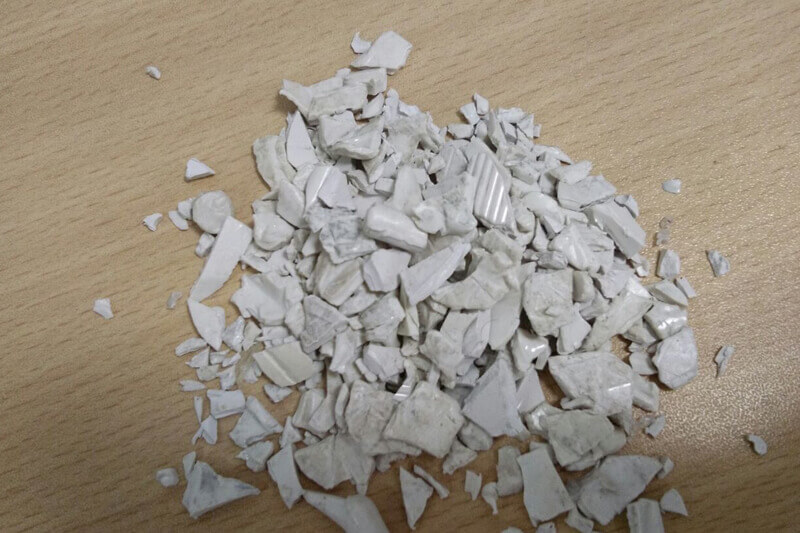

Polyetherimide (PEI)
Polyetherimides (PEI) belong to the polyimides and is polymer with imide and ether groups in the main chains. They are resistant to high temperatures, transparent and have a golden yellow color. PEI is one of the high-performance plastics. Polyetherimides (PEI) are sold in pure form and with various additives (glass fibers, carbon fibers). Polyetherimides are mainly processed by injection molding.
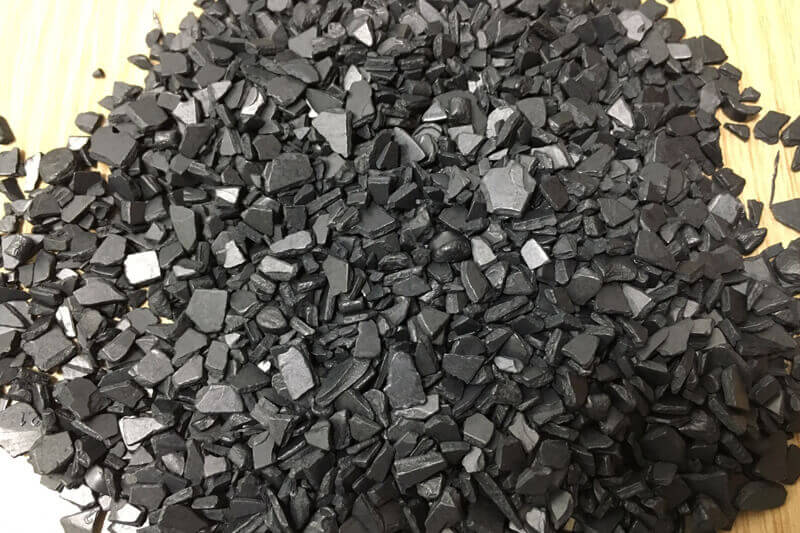

Polyetheretherketone (PEEK)
Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) is a high-temperature-resistant thermoplastic and belongs to the high-performance plastics. PEEK melts at a very high temperature of 335 ° C and compared to most other thermoplastics it can be molded in the liquid state by injection molding or by extruder. When solid, PEEK can be machined, turned or drilled with a mill.

Polyphenylsulfone (PPSU)
Polyphenylsulfones (PPSF or PPSU) are high-performance plastics, which usually consist of aromatic rings. Polyphenylsulfones (PPSU) are heat and chemical resistant suitable for automotive, aerospace and sanitary applications. Polyphenylsulfones have no melting point, reflecting their amorphous nature.
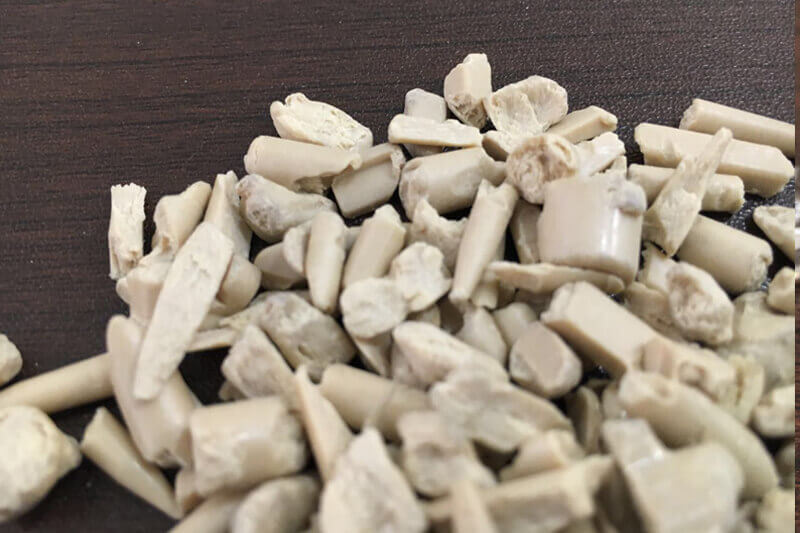

Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS)
Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) is an organic polymer consisting of aromatic rings linked by sulfides. Polyphenylene sulfide is a engineering plastic commonly used today as a high performance thermoplastic.
Synthetic fibers and textiles made from PPS are resistant to chemical and thermal attack. Isolated PPS can be converted to the semiconducting form by oxidation. PPS can be formed, extruded or machined to tight tolerances.

Polyethersulfone (PES)
LPolyethersulfones (PESU or PES) are a high performance thermoplastic belonging to the group of polysulfones. It is transparent, resistant to hydrolysis and chemically resistant. PES is mainly used for thermally highly stressed parts (medical devices, automotive and aircraft construction, electrical and electronic components).
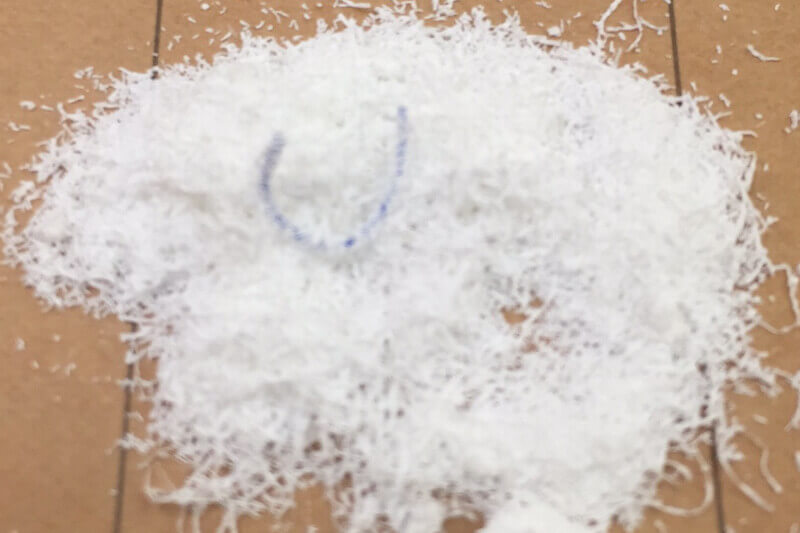

Polyarylsulfones (PSU)
Polyaryl sulfones (PSU) are thermoplastics belonging to the group of polysulfones. Polysulfones are translucent and light brown in color due to their amorphous molecular structure. Polyaryl sulfone (PSU) is a high performance plastic with high mechanical strength and rigidity.
PSU has a high continuous service temperature, the outstanding properties of the material include good creep resistance over a wide temperature range, dimensional stability and good chemical compatibility.

Polyvinyl Difluoride (PVDF)
Polyvinylidene fluoride or polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) is a non-reactive thermoplastic fluoropolymer made by the polymerization of vinylidene difluoride. PVDF is a special plastic for applications requiring the highest levels of purity and resistance to solvents, acids and hydrocarbons. PVDF has a lower density compared to other fluoropolymers such as polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon).

Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP)
Liquid crystal polymers (LCP) are a class of aromatic polymers. They are extremely non-reactive, inert and very fire-resistant. The superior properties of LCPs make them particularly suitable for automotive sector such as; Transmission components, pump components, coil forms and sunlight sensors as well as sensors for car safety belts.

Ethylene Tetrafluoroethylene (ETFE)
Ethylene tetrafluoroethylene (ETFE) is a fluorine-based plastic. It is designed to have high corrosion resistance and strength over a wide temperature range.
ETFE has a relatively high melting temperature, excellent chemical, electrical and high energy radiation resistance. ETFE film is self-cleaning (due to its non-stick surface) and recyclable.

Fluoroethylene Propylene (FEP)
Fluoroethylene propylene (FEP) is a copolymer of hexafluoropropylene and tetrafluoroethylene. It differs from PTFE in that it is meltable with conventional injection molding and screw extrusion techniques. FEP is very similar to PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) and PFA (perfluoroalkoxy polymer). FEP and PFA both share the useful properties of PTFE. FEP is softer than PTFE and melts at 260 ° C. It is highly transparent and sun resistant.

Polytetrafluorethylene (PTFE)
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a linear polymer of fluorine and carbon. PTFE is often referred by the trade name Teflon from DuPont. PTFE belongs to the class of polyhalogenolefins. It is one of the thermoplastics, although it also has properties that require a thermosetting plastics typical processing.
Super Absorbent Polymer (SAP)
Superabsorbents (superabsorbent polymers, SAP) are plastics that are capable of absorbing liquids many times their own weight. Upon absorption of the liquid, the superabsorbent swells and forms a hydrogel. Low-density SAPs generally have a higher absorption capacity and swell more. These types of SAPs also have a softer and stickier gelation.

Cellulose Acetate (CA)
Cellulose acetate is the acetate ester of cellulose. Cellulose acetate (CA) is considered a thermoplastic but is a modified natural product.
Cellulose acetate is used as a film base in photography, as a component in some coatings and as a frame material for eyeglasses. It is also used as a synthetic fiber in the manufacture of cigarette filters and playing cards.

HYDROCARBON RESIN
Hydrocarbon Resin is an aromatic hydrocarbon used in industrial applications. It is a kind of thermal plasticizing hydrocarbon resins. It has a sticky effect and is suitable for use in paint, printing ink, adhesives, rubber and other areas where tackiness is required.

Polylactide (PLA)
Polylactides, also called polylactic acids (PLA), are synthetic polymers that are among the group of polyesters. They are composed of many, chemically bonded lactic acid molecules. PLA can be deformed by heat and is therefore a thermoplastic.

Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA)
Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) are polyesters that are produced in nature by numerous microorganisms. PHA is biodegradable and is used to manufacture bioplastics. Polyhydroxyalkanoates can be either thermoplastic or elastomeric materials. The mechanical properties and biocompatibility of PHA can be altered by blending or modifying with other polymers, enzymes, and inorganic materials allowing the material a wide range of applications.

Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB)
Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) is a polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA), a polymer of the polyester class. PHB is one of the biodegradable plastics. PHB belongs to the thermoplastic polyester and is therefore deformable with heat.
